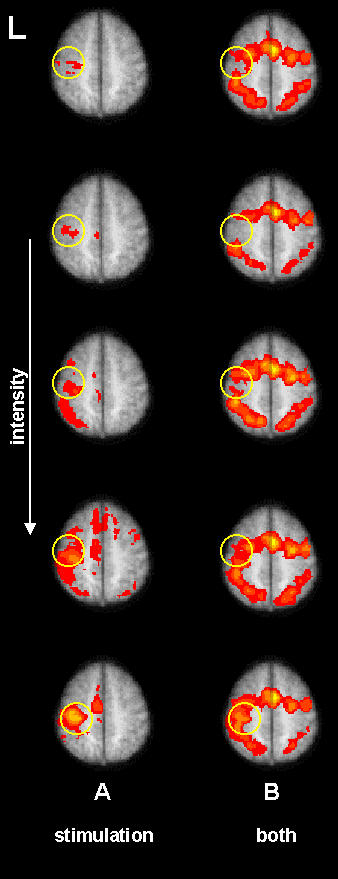

Attention to electrical somatosensory stimulation of the median nerve was explored with a distraction paradigm. Subjects were given sensory stimulation of increasing intensity with and without distraction by concurrent performance of a counting task. Left column (A) shows increasing activation with increasing stimulation intensity. The primary somatosensory cortex (SI) is within the yellow circle. The right column (B) shows activation when stimulation is applied during counting task performance. Additional activation is seen in counting areas (bialteral parietal cortex, pre SMA). However, the sensory activation in SI is reduced (within yellow circles). Electrical somatosensory evoked potentials were measured during the same tasks and, unlike the FMRI signal from SI, no attentional modulation was observed in the early SEP from S1. (see Arthurs O, Johansen-Berg H, Boniface S, Matthews PM (2002) Attention differentially modulates functional magnetic resonance imaging and evoked potential amplitude in human somatosensory cortex. 8th International conference for Functional Mapping of the Human Brain, Sendai, Japan.